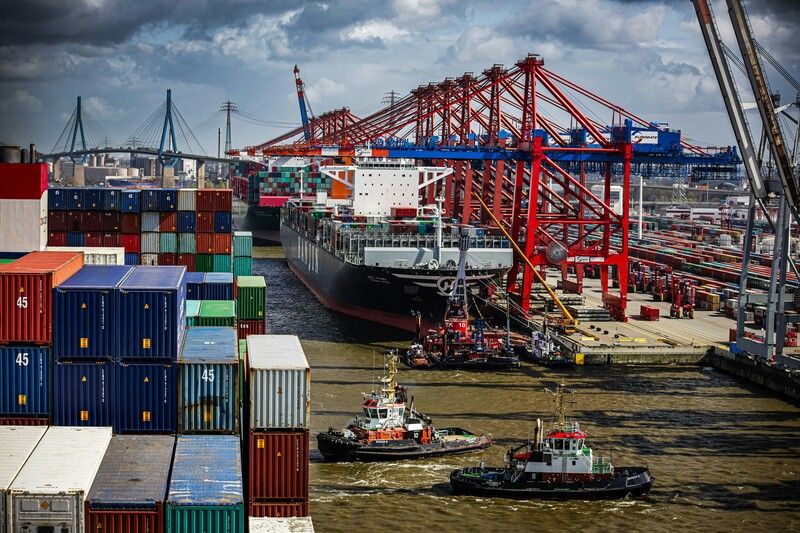

Introduction: A Shifting Global Economic Landscape
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has announced a significant downward revision of its global growth projections for 2025, citing escalating U.S.-China trade tensions and rising protectionism as primary factors. While the IMF does not foresee a global recession, it warns of increased inflation and financial market stress in certain countries. This adjustment reflects the growing uncertainties in the global economic environment.
Trade Tensions and Protectionism: Key Drivers of Economic Slowdown
The IMF attributes the revised growth forecasts to the intensifying trade disputes between major economies, particularly the United States and China. The imposition of tariffs and retaliatory measures has disrupted global supply chains, leading to inefficiencies and higher costs. IMF Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva emphasized that these trade barriers are “like pouring cold water on an already-lukewarm world economy,” highlighting the detrimental impact on global trade and economic activity.
Inflationary Pressures and Financial Market Volatility
In addition to trade disruptions, the IMF anticipates rising inflation in some countries as a result of increased import costs and supply chain bottlenecks. The higher consumer prices globally, coupled with conflicts in the Middle East and Europe, contribute to the “far from good enough” medium-term growth prospects. These factors are expected to exert pressure on household budgets and corporate profit margins, potentially leading to reduced consumer spending and investment.
Financial markets are also experiencing increased volatility due to the uncertain trade environment. Movements in U.S. Treasury yields and other indicators suggest heightened investor apprehension. The IMF cautions that persistent uncertainty could trigger financial market stress, undermining investor confidence and potentially leading to capital outflows from emerging markets.
Debt Levels and Investment Challenges
The IMF’s concerns are further compounded by the rising levels of global public debt, projected to reach $100 trillion by the end of the year, or 93% of global GDP. This mounting debt burden poses significant challenges for countries in servicing their obligations and financing essential investments. The IMF warns that low growth and high debt could impair efforts to reduce poverty and address critical issues such as climate change and infrastructure development.
Policy Recommendations and the Path Forward
In response to these challenges, the IMF advocates for continued economic reforms, flexible monetary policies, and enhanced global cooperation. Georgieva urges countries to work toward reducing tariffs and other trade barriers to foster a more open and efficient global trading system. She also emphasizes the importance of maintaining price stability through prudent monetary policies and addressing structural issues that hinder economic growth.
The IMF’s updated World Economic Outlook, to be released soon, will provide a more detailed analysis of these developments and their implications for the global economy. As finance ministers and central bank leaders prepare to converge on Washington for the IMF and World Bank spring meetings, the focus will be on finding collaborative solutions to mitigate the risks posed by escalating trade tensions and economic uncertainties.
Conclusion: Navigating Uncertainty in a Complex Global Economy
The IMF’s revised growth forecasts underscore the interconnectedness of global economies and the profound impact of trade policies on economic stability. While the outlook remains cautious, the IMF’s call for cooperative efforts and policy reforms offers a pathway to navigate the current challenges. As the global community faces these economic headwinds, the emphasis will be on fostering resilience, promoting sustainable growth, and ensuring that economic progress benefits all nations equitably.

































Leave a Reply