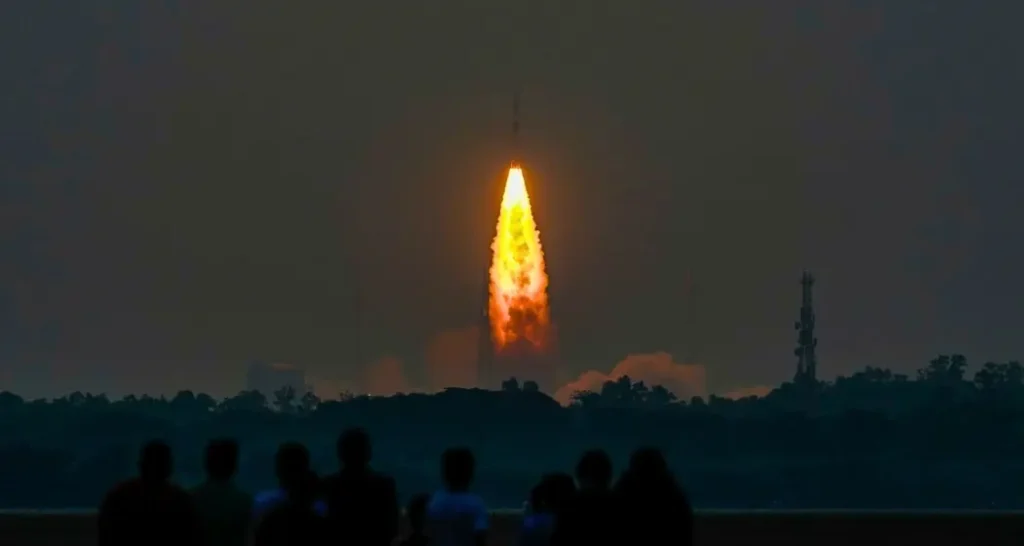

A Rare Setback in ISRO’s Journey
On May 18, 2025, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) faced an unexpected challenge when its 101st satellite launch, PSLV-C61 carrying the EOS-09 Earth Observation Satellite, failed to reach its intended orbit. The mission, launched from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, initially proceeded smoothly, with the first and second stages performing as expected. However, a technical anomaly in the third stage led to the mission’s premature termination, marking a rare setback for ISRO’s otherwise commendable track record.
Understanding the Mission’s Significance
EOS-09, also known as RISAT-1B, was designed to enhance India’s Earth observation capabilities. Equipped with a C-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR), the satellite aimed to provide high-resolution imaging of the Earth’s surface, crucial for applications such as agriculture monitoring, disaster management, and national security. Its ability to capture images irrespective of weather conditions or time of day was expected to be a significant asset for various sectors relying on timely and accurate data.
The Technical Anomaly Explained
The PSLV-C61 mission involved a three-stage launch vehicle: solid fuel in the first stage, liquid fuel in the second, and a cryogenic engine in the third. While the first two stages executed flawlessly, the cryogenic upper stage failed to ignite, leading to the mission’s failure. Cryogenic engines, which use liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, are known for their efficiency and high specific impulse. However, they are also complex and sensitive to technical anomalies, making them challenging to manage.
Reactions from the Scientific Community
The failure has drawn attention from various quarters. Former ISRO Chairman G. Madhavan Nair expressed shock over the incident but emphasized ISRO’s resilience, stating that the organization would learn from this experience and continue to advance. Experts have highlighted the complexity of the cryogenic stage, noting that such anomalies, while unfortunate, are part of the learning curve in space exploration.
ISRO’s Response and Future Plans
In response to the failure, ISRO has constituted a Failure Analysis Committee to investigate the cause of the anomaly in the cryogenic stage. The organization remains committed to its mission of advancing space technology and is expected to incorporate the findings from this investigation into future missions. Despite this setback, ISRO’s track record of successful launches and its ongoing projects continue to inspire confidence in its capabilities.
Conclusion
While the failure of the EOS-09 mission is a setback, it underscores the inherent challenges of space exploration. ISRO’s proactive approach to investigating the anomaly and its history of resilience suggest that this will be a temporary hurdle. As the organization continues to push the boundaries of space technology, the lessons learned from this mission will undoubtedly contribute to its future successes.

































Leave a Reply