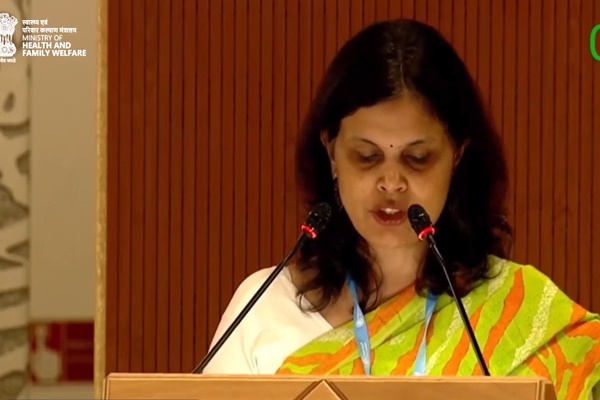

Championing Universal Health Coverage
At the 78th World Health Assembly held in Geneva, India reaffirmed its unwavering commitment to global health equity under the theme “One World for Health.” Union Health Secretary Punya Salila Srivastava, leading the Indian delegation, highlighted the nation’s transformative strides in healthcare, notably through the Ayushman Bharat initiative. This flagship program has significantly expanded access to comprehensive healthcare, improved infrastructure, provided financial protection for advanced treatments, and accelerated digital health adoption, paving the way toward Universal Health Coverage.
Advancements in Maternal and Child Health
India’s efforts in maternal health, family planning, and the reduction of childhood mortality and stillbirths have garnered international recognition. Global bodies, including the United Nations Population Fund and the UN Inter-Agency Group, have acknowledged these achievements. The nation’s commitment to enhancing maternal and child health continues to be a cornerstone of its public health strategy.
Eliminating Infectious Diseases
In a significant public health milestone, India was recently certified as Trachoma-Free by the World Health Organization (WHO). This achievement underscores the country’s dedication to eliminating infectious diseases. India is also actively working towards the eradication of other diseases such as tuberculosis, leprosy, lymphatic filariasis, measles, rubella, and kala-azar, reflecting its comprehensive approach to public health.
Expanding Health Coverage and Medical Education
A major policy step was the extension of health coverage under the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana to all citizens above 70, regardless of economic status. Additionally, India has doubled the number of medical colleges from 387 to 780 in the past decade, aiming to train future healthcare professionals and address the growing demand for medical services.
Advocating for Global Health Frameworks
India reiterated its strong support for a legally binding global health framework that enhances international cooperation while respecting national sovereignty and capacities. The country emphasized the need for such a framework to ensure equitable access to medical countermeasures, timely and transparent data and pathogen sharing, and promote technology sharing and capacity building, particularly for the Global South.
Conclusion
India’s participation in the 78th World Health Assembly underscores its leadership in promoting global health equity. Through comprehensive healthcare initiatives, international collaborations, and a commitment to addressing social determinants of health, India continues to play a pivotal role in shaping a healthier, more equitable world.

































Leave a Reply