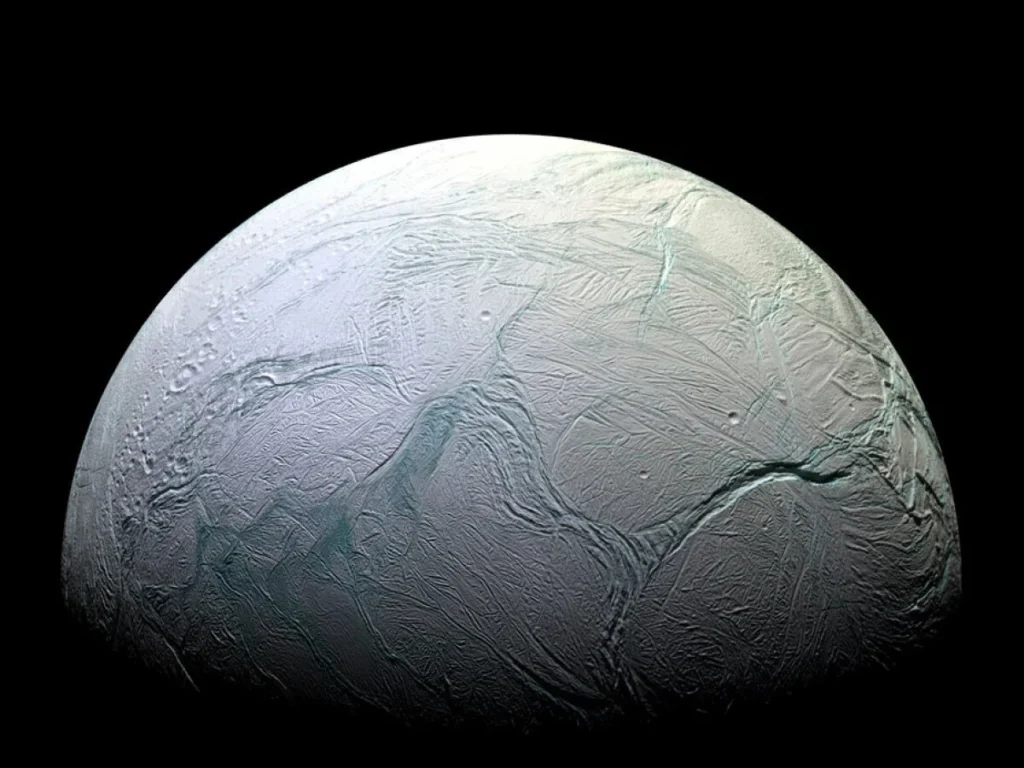

In an extraordinary revelation by astronomers, Saturn’s moon Enceladus has been identified as a celestial body possessing all the necessary components for life. This significant discovery comes in the wake of observations made by the James Webb Space Telescope, which detected water plumes soaring thousands of kilometers from Enceladus’s surface. The latest findings, spearheaded by a German-led international research team and published in the journal Nature, have pinpointed Phosphorus in the icy grains emitted by Enceladus, marking a pivotal moment in the search for extraterrestrial life.
Phosphorus, a crucial element for numerous biological processes, has been found in abundance in the subsurface ocean of Enceladus, encapsulated within salt-rich ice grains that are expelled into space. This discovery draws on the data returned by the Cassini spacecraft, which dedicated 13 years to the exploration of Saturn and its moons. During its mission, Cassini’s Cosmic Dust Analyzer instrument sampled icy particles from Saturn’s E ring, shedding light on the moon’s intriguing composition.
Enceladus’s ice grains had previously been analyzed for their rich mineral content and complex organic compounds, laying the groundwork for the potential synthesis of amino acids—key building blocks of life as we understand it. The presence of elements such as sodium, potassium, chlorine, and carbonate-containing compounds had already hinted at the moon’s complex chemical makeup.
Frank Postberg, the planetary scientist leading the study, expressed the significance of the discovery, stating, “We previously found that Enceladus’s ocean is rich in a variety of organic compounds. But now, this new result reveals the clear chemical signature of substantial amounts of phosphorus salts inside icy particles ejected into space by the small moon’s plume. It’s the first time this essential element has been discovered in an ocean beyond Earth.”
This groundbreaking discovery not only enriches our understanding of Enceladus but also expands the horizons of our search for life beyond Earth, offering a glimmer of hope that the vast, cold reaches of space may yet harbor the conditions necessary for life to flourish.

































Leave a Reply