
The phenomenon of global warming has emerged as one of the most pressing environmental challenges of the 21st century. Characterized by a steady increase in Earth’s average surface temperature, this crisis is attributed largely to human activities, notably the burning of fossil fuels which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat from the sun, leading to a warming effect known as the greenhouse effect. This warming is not without consequence, significantly impacting the planet’s ice reserves, among other environmental catastrophes.
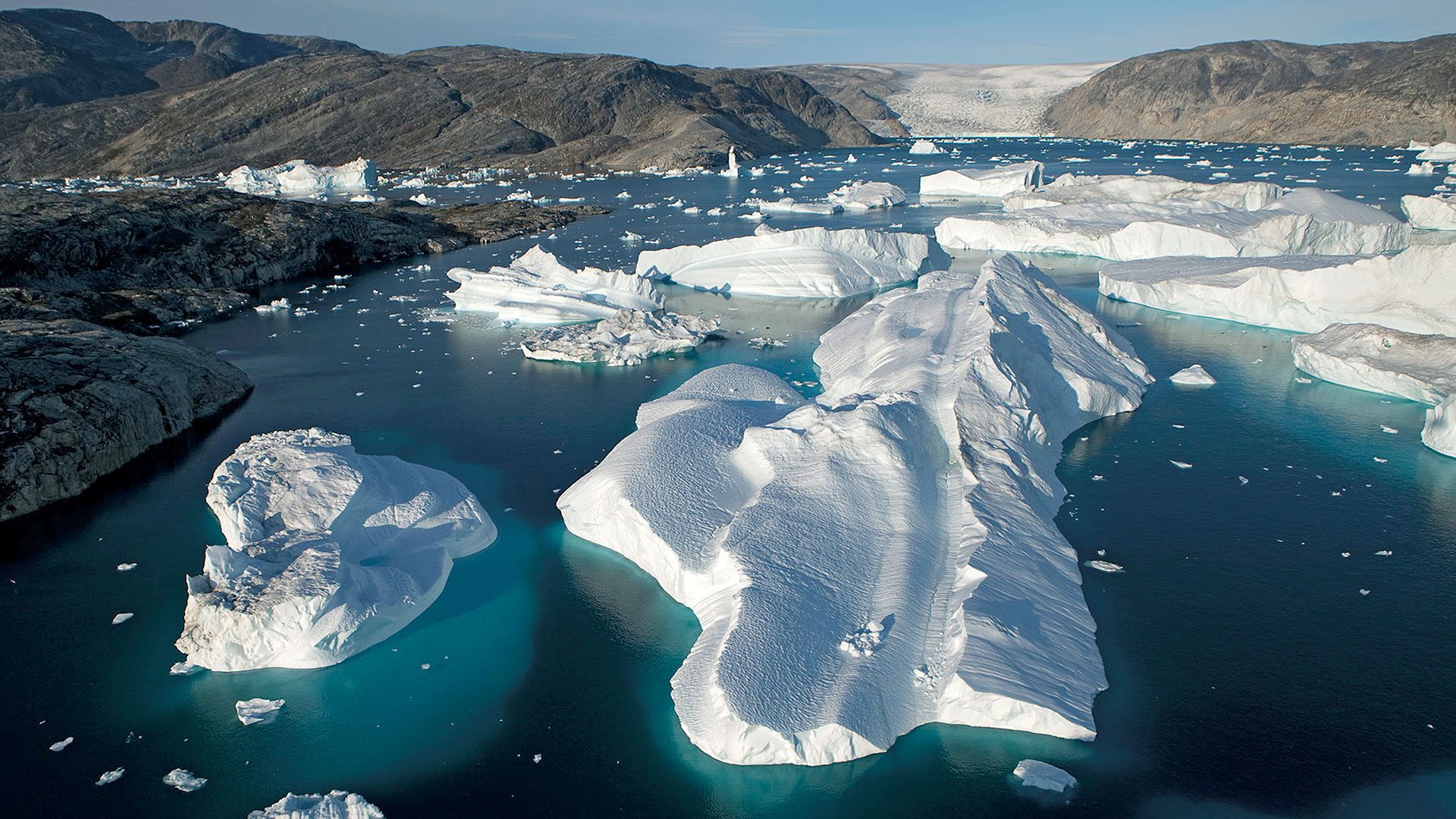
The melting of ice caps and glaciers is one of the most visible and alarming signs of global warming. Polar regions, home to vast ice sheets that have existed for millennia, are experiencing unprecedented melt rates. In Antarctica and Greenland, ice sheets are shrinking at an accelerating pace, contributing to rising sea levels worldwide. This meltwater not only increases sea levels but also disrupts marine ecosystems and threatens coastal communities with increased flooding and storm surges.
Beyond the poles, mountain glaciers around the world, from the Himalayas to the Rockies, are receding at alarming rates. This not only leads to the loss of iconic landscapes but also affects freshwater availability for millions of people. Glaciers act as natural freshwater reservoirs, releasing water during warmer months to support rivers and lakes essential for drinking water, agriculture, and hydroelectric power.
The consequences of ice melt due to global warming are far-reaching and interlinked, affecting not just sea levels but also weather patterns, wildlife habitats, and global climate systems. The feedback loops created by ice loss exacerbate the warming; for example, as white ice, which reflects sunlight, is replaced by darker water or land, more heat is absorbed, further increasing temperatures.
Addressing the root causes of global warming is critical to slow the rate of ice melt and mitigate its impacts. This requires a concerted global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, transition to renewable energy sources, and improve energy efficiency. While the challenge is daunting, the urgency of the situation demands action now to safeguard our planet for future generations. The melting ice serves as a stark reminder of the tangible effects of global warming and the need for immediate and sustained efforts to combat this existential threat.

































Leave a Reply