India’s economic trajectory is deeply tied to the fiscal health of its states. Recognizing the need for effective financial management, the NITI Aayog released the latest Fiscal Health Index (FHI) to evaluate state finances and guide reforms.
Key Dimensions of the Fiscal Health Index (FHI):
The FHI aggregates state performance across five crucial sub-indices:
- Quality of Expenditure: Measures the share of developmental spending and capital investment in total expenditure, reflecting long-term growth priorities.
- Revenue Mobilisation: Assesses states’ capacity to generate their own revenue proportionate to economic output.
- Fiscal Prudence: Highlights gaps between revenue and expenditure, signaling dependency on borrowing.
- Debt Index: Evaluates debt burdens through interest payments and outstanding liabilities.
- Debt Sustainability: Balances economic growth against debt servicing needs, ensuring a sustainable fiscal framework.
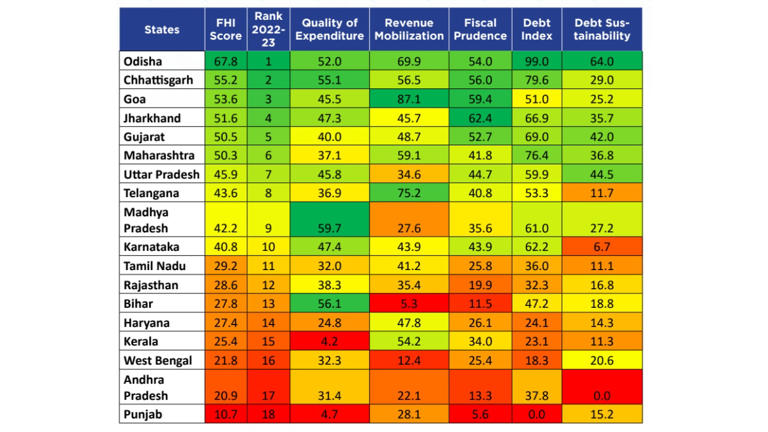
2022-23 Fiscal Health Rankings
Odisha stood out as India’s most fiscally stable state, while Punjab lagged with the lowest score. The rankings underline significant disparities among states in fiscal management.
| State | FHI Score | Rank | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| Odisha | 67.8 | 1 | Debt sustainability, revenue mobilisation |
| Chhattisgarh | 55.2 | 2 | Balanced expenditure, fiscal prudence |
| Goa | 53.6 | 3 | Revenue mobilisation efficiency |
| Punjab | 10.7 | 18 | Struggles in debt sustainability, revenue |
Key Findings and Concerns:
- Odisha’s Success:
- Exemplary performance in managing debt and mobilising revenue ensures its position as the top-ranked state.
- Underperforming States:
- Punjab, Kerala, and Andhra Pradesh are under severe fiscal stress due to escalating debt and poor revenue generation.
- Balanced Performers:
- States like Chhattisgarh and Goa highlight the benefits of balanced fiscal strategies.
Implications for Policymakers
The FHI Report emphasizes prudent fiscal policies:
- States need to optimise developmental expenditures to fuel long-term growth.
- Focus on sustainable debt practices to prevent fiscal instability.
- Enhance revenue mobilisation efforts, reducing reliance on central assistance.
By adopting these reforms, states can boost financial stability, aiding in India’s overarching goal of sustained economic growth and national development.








































Leave a Reply