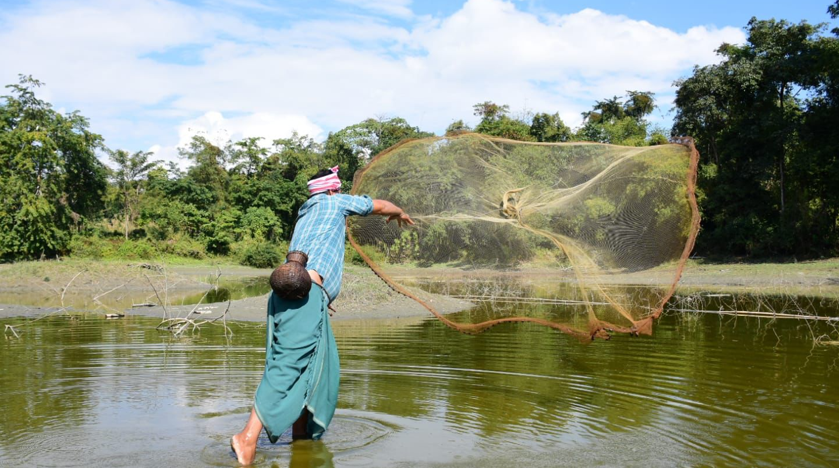

- Increased Flooding: Climate change has made Assam’s floods more severe, causing soil erosion, biodiversity loss, and displacement in the Brahmaputra floodplains.
- Agricultural Challenges: Unpredictable floods damage crops, wash away fertile soil, and disrupt planting seasons, leading to economic and food security issues.
- Adaptation Solutions: Measures like flood-resistant crops, improved drainage, and floodplain zoning are vital for Assam’s resilience against climate impacts.
The Impact of Climate Change on Assam’s Floodplains and Agriculture
Assam, known for its fertile floodplains along the Brahmaputra River, is facing unprecedented challenges due to climate change. With rising temperatures, shifting monsoon patterns, and glacial melt, the region’s vulnerability to floods has significantly intensified. This shift affects not only Assam’s agriculture and food security but also poses broader environmental challenges.
Increased Flooding and Environmental Impact
Flooding is a natural part of Assam’s ecosystem and historically has nourished the floodplains with nutrient-rich silt that supports crops like rice and tea. However, climate change has led to unpredictable and severe flood patterns that are far more challenging to manage. The Brahmaputra River, fed by Himalayan glaciers, has become increasingly volatile as glacial melt increases and monsoon patterns become erratic.
The consequences of these intensified floods are substantial. Floodwaters often lead to prolonged waterlogging, which causes significant soil erosion, loss of fertile soil, and destruction of habitats essential for biodiversity. For example, frequent and intense floods disrupt habitats for various wildlife species, forcing them into less suitable areas or even resulting in population decline. Local communities are also severely impacted, with widespread displacement and damage to infrastructure. Villages and towns that previously managed seasonal floods now find themselves at risk of recurrent, destructive flooding, creating both social and environmental crises.
Challenges to Assam Agriculture
Assam’s agriculture has traditionally thrived on the silt deposits from regular floods, which enriched the soil and sustained crop productivity. However, the new climate dynamics are eroding this foundation. Prolonged and severe floods destroy standing crops, wash away fertile topsoil, and delay planting seasons, which disrupts the agricultural cycle. Crops like rice, which requires careful timing and optimal water conditions, are particularly affected, resulting in decreased yields and increased food insecurity in the region.
The economic toll on farmers is substantial, with many facing losses year after year as floods become more intense. Without the time and resources to adapt, farmers are caught in a cycle of reduced productivity and financial instability. This impact is not limited to rural areas; the economic consequences ripple across Assam, affecting food prices, local employment, and overall state income.
Adaptation and Sustainable Solutions
In response to these challenges, proactive climate adaptation strategies are essential for Assam. Some of these include:
- Flood Forecasting and Early Warning Systems: Improved flood forecasting technologies can help local communities prepare and respond effectively to upcoming floods. Early warning systems allow people to safeguard livestock, evacuate vulnerable areas, and minimize losses.
- Strengthening Embankments and Drainage Systems: Reinforcing embankments along rivers and improving drainage systems are critical to managing water flow and preventing prolonged waterlogging in agricultural fields.
- Flood-Resistant Crop Varieties and Crop Diversification: Introducing flood-resistant varieties of staple crops such as rice can help minimize losses during heavy flooding. Crop diversification can also offer farmers resilience by reducing dependence on single crops that are highly susceptible to floods.
- Community Awareness and Training: Engaging local communities through awareness programs about climate risks and adaptation practices empowers people to make informed decisions and adopt sustainable practices.
- Sustainable Farming Practices and Floodplain Zoning: Implementing sustainable farming methods and establishing zoning regulations in flood-prone areas can help manage agricultural land more effectively and prevent further degradation of soil quality.
Building Resilience Against Climate Change
The urgent need for climate adaptation strategies in Assam is clear. Sustainable practices and infrastructural improvements can strengthen Assam’s floodplains and agriculture against the increasing impacts of climate change. By adopting climate-resilient strategies, Assam can work toward securing food production, protecting biodiversity, and ensuring a stable livelihood for its communities.
Conclusion The situation in Assam reflects the broader challenges that climate change poses to vulnerable regions worldwide. The intensification of floods and the resulting challenges to agriculture and community resilience underscore the need for immediate action. Investments in climate adaptation and infrastructure, along with community-centered approaches, will be essential for Assam to safeguard its environment, agriculture, and future against the growing threat of climate change.

































Leave a Reply